Energy Efficiency & Cost Savings
Are you looking to get more out of your home cooling and heating system? Heat pumps have come a long way from the basic models of the past, and now many of them boast cutting-edge technology and smart features that can help you cut back on energy consumption and save on your utility bills, all while experiencing year-round comfort.
If it’s time to upgrade your home’s old HVAC system or you’re exploring more energy efficient options, a modern heat pump with some key bells and whistles could be the smarter, more sustainable choice. Here, we’ll take a look at how heat pumps work to keep your home both warm and cool, what type of heat pump could be right for your needs, and which innovations and features are most important to maximize your savings.
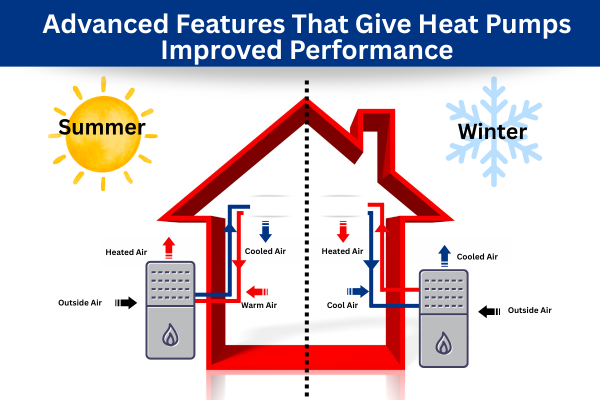
Heat pumps are a smart and energy-efficient way to both heat and cool your home. Instead of simply generating heat like a traditional furnace, heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another, so they can pull double duty, playing the role of both a furnace and an air conditioner. In the winter, a heat pump will pull heat from the outdoor air and bring it inside. In the summer, they kick into the opposite gear, removing heat from the indoor air in your home and releasing it outside. This process uses less energy than systems that rely on burning fuel, like natural gas, making them an eco-friendly solution.
Heat pumps generally have a higher seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) rating, indicating that they consume less electrical energy over a cooling season than a traditional central air conditioner. This is one part of a heat pump’s overall energy efficiency ratio (EER) for cooling. As for heating, the measure used is the heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF). This metric looks at how efficient the heat pump is during the heating season by dividing its heating output (BTUs) by the total electricity consumed (kWh). The efficiency of a heat pump is hard to argue, but how exactly can it leverage heat energy to keep your home comfortable all year long?
One of the key features that sets heat pumps apart is the reversing valve. This innovative component allows the system to switch between heating and cooling modes effortlessly, so your home stays comfortable no matter what the outdoor temperature is.
In heating mode, the heat pump absorbs the heat in the outside air and moves it inside. When the temperatures rise and cooling is needed, the reversing valve switches the flow, so the pump extracts heat inside your home and forces it out. This built-in versatility is the foundation of the heat pump, and is what makes it a popular all-season HVAC option.
To better understand how heat pumps work, it helps to know the major parts you’ll find inside:
Heat pumps come in several different types, each designed for optimal performance in specific settings or climates. If you’re considering a heat pump for your home, it’s helpful to know the different options available, and how they might work in your location. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of heat pumps and what makes each of them unique:
Air-source heat pumps are the most common sort. They work by transferring heat between the inside of your home and the outside air. In many places, they are able to efficiently heat your home in winter and cool it down in summer. These systems are so popular because they’re cost-effective, relatively easy to install, and ideal for moderate climates. Newer models are also better at keeping up with space heating in colder temperatures.
You may also hear ground-source heat pumps referred to as geothermal heat pumps. These systems use the steady temperature of the earth below us to heat and cool homes. They pull existing heat from the ground during the winter and release it back into the ground in summer. Ground-source heat pumps are extremely energy efficient and can significantly reduce your energy costs over time. The upfront installation costs, however, are usually considerably higher, especially due to the amount of digging involved. In spite of this, geothermal systems can offer long-term savings and durability.
Water-source heat pumps transfer heat to and from a nearby water source, which may be a lake, a pond, or an underground water well. They function in the same way a geothermal heat pump does, but rely on water rather than soil. Of course, these types of heat pumps can only be installed in properties located near a stable water source, limiting their availability, but in those areas, they are considered highly efficient.
Thanks to major advancements in technology, cold climate heat pumps are specifically designed to operate efficiently in regions that experience extreme winter weather. These systems use enhanced compressors and improved refrigerant flow to gather heat from very cold outdoor air, which is something the heat pumps of the past struggled to do. For homeowners in colder parts of the country, these newer models make heat pumps a more viable and efficient option all year long.
Choosing the right type of heat pump and the right energy source for your location is the first step to making your home comfortable and energy efficient year-round. Once you know what’s available in your area, you can begin vetting heat pumps according to their features. Recent technological improvements have enhanced the year-round performance of heat pumps. These particular features can help you get the most comfort, energy savings and versatility out of such a unique appliance.
The compressor in a heat pump alters the pressure of the refrigerant, which allows it to carry heat to and from your home. The newer Scroll compressor operates more efficiently and quietly than piston compressors, and since it has fewer moving parts, it also lasts longer. A dual-speed compressor runs at two different speeds, and when temperatures are mild throughout the year, it will run on a lower speed most of the time, which lowers energy consumption.
Some heat pumps can switch from harvesting outdoor air to a compatible combustion furnace equipped with a burner that uses gas or propane, offering the best of both worlds. The heat pump handles the job on milder days, with the furnace kicking in only when temps drop too low for too long. This smart setup automatically switches between systems to maximize comfort and energy savings.
A system that features a variable-speed motor in the indoor blower can adjust the speed of the fan to meet your home’s air conditioning needs. When it requires just a few degrees of heating or cooling, it’ll run at a lower speed, which is quieter and circulates conditioned air more thoroughly. These types of motors can be set to run nearly continuously, and because they’re operating at a lower speed, more air passes through the air filter daily. Indoor air quality will also improve as more airborne particulates are trapped by the heat pump’s high efficiency pleated air filter.
Many modern heat pumps are compatible with smart thermostats, which adjust temperature settings automatically based on your habits, preferences, and even weather forecasts. When connected to your HVAC system, a smart thermostat helps reduce unnecessary run times and provides detailed data on your energy usage. It’s a simple upgrade that can lead to significant long-term savings, all while making comfort control more convenient.
If you have areas of your home that are warmer or cooler than others, zoning technology can help. Some heat pump systems allow you to divide your home into separate zones, each with its own temperature control, called mini-split system. A mini-split utilizes several air handlers in different locations for ductless heating and cooling. This makes it easy to customize comfort levels room by room, avoid wasting energy on unused areas, and reduce monthly utility costs. You can also use a mini-split in conjunction with a standard heat pump that uses your home’s existing ductwork.
When temperatures drop below freezing, moisture can freeze on the outdoor coil of your heat pump and affect performance. Advanced models come with automatic defrost controls that detect frost buildup and temporarily switch the system into cooling mode to melt it off. This prevents long-term strain on the system and keeps it running efficiently during cold spells.
Modern heat pumps often include noise-reduction features such as sound-dampening insulation, high-efficiency fan blades, and variable-speed compressors. These upgrades aren’t just nice for your comfort; they also help keep your neighborhood and your home quieter.
If you’re in the market for an efficient heat pump that can reduce your emissions and lower your electric bills, Airtron is here to help you find the right heat pump technology for your home and location. We’ll help you understand your available heat sources and get you up and running in time for cooling or heating season. We can also help you learn about possible incentives and rebates that could save you even more. Check out our heating installation services and contact us to learn more!